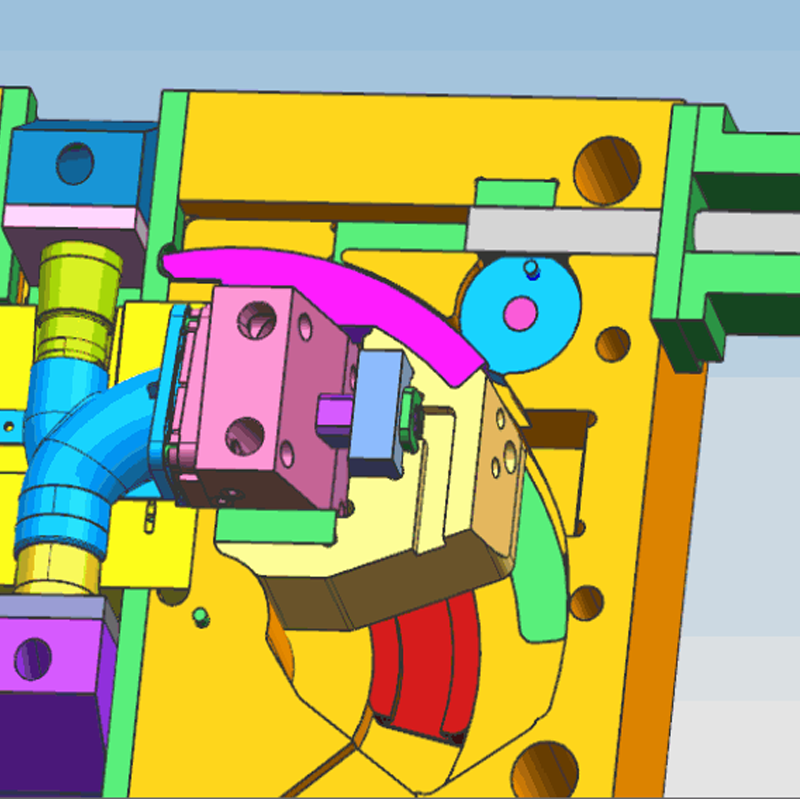
Injection molding is a critical process in modern manufacturing, used to produce everything from everyday household items to intricate components for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. Understanding the different types of injection molds is essential for optimizing production efficiency, product quality, and cost-effectiveness. Injection molds come in various forms, each designed to meet specific requirements based on the complexity, function, and features of the final product.
In this post, we will explore eight common types of injection molds, each defined by its structural characteristics and functionality. By understanding these different mold types, manufacturers can select the right mold for their product, ensuring high-quality output and an efficient production cycle.
-
Single-Parting Surface Injection Mold (Two-Plate Mold)
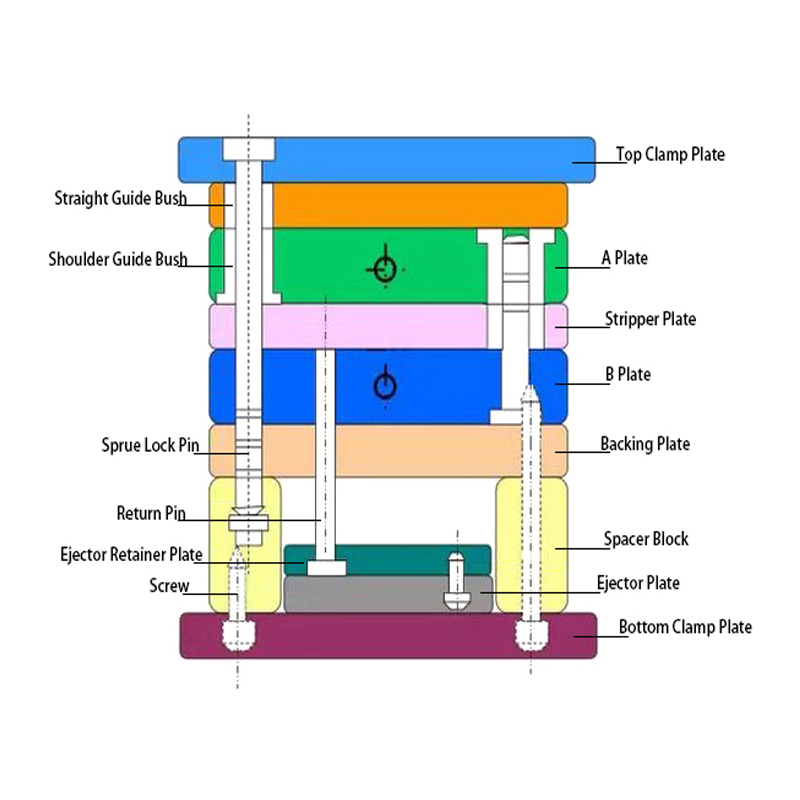
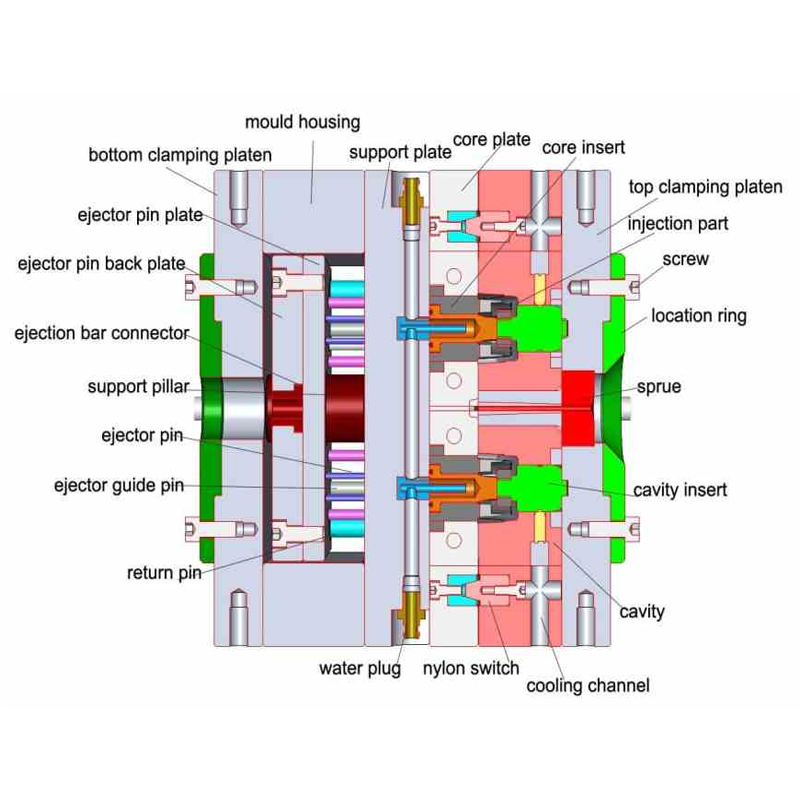
The single-parting surface mold, commonly referred to as the two-plate mold, is the most straightforward and widely used type of injection mold. This mold features two primary sections: the fixed mold plate and the movable mold plate. When the mold opens, the two plates separate, allowing the ejection of the molded part.
This simple design makes it highly adaptable, capable of producing single-cavity or multi-cavity parts depending on the production requirements. Its simplicity also makes it easy to maintain and cost-effective to manufacture, which is why it is favored for most basic injection molding applications. It’s an ideal choice for manufacturers looking for a reliable, economical solution for mass production.
-
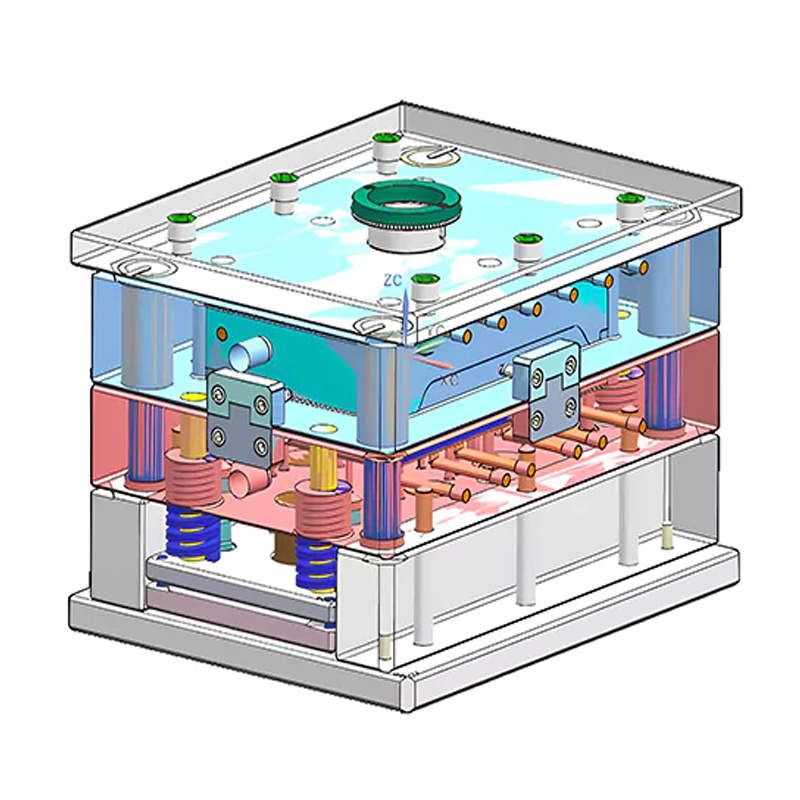
Double-Parting Surface Injection Mold (Three-Plate Mold)
The double-parting surface mold, also known as the three-plate mold, is more complex than the two-plate mold. As the name suggests, this mold features three plates: the fixed mold plate, the movable mold plate, and a middle plate. The middle plate serves as an additional component that helps separate the gating system, which includes gates and runners, during the molding process.
The three-plate mold is typically used in more complex designs where multiple cavities or a point gate feeding system are required. When the mold opens, the middle plate moves a fixed distance away from the fixed mold plate along guide pillars. This movement allows for the separation of the runner system, which is essential for the removal of the molded part without interference from the runners. The three-plate mold is commonly used in multi-cavity applications and products that require more intricate gating systems.
-
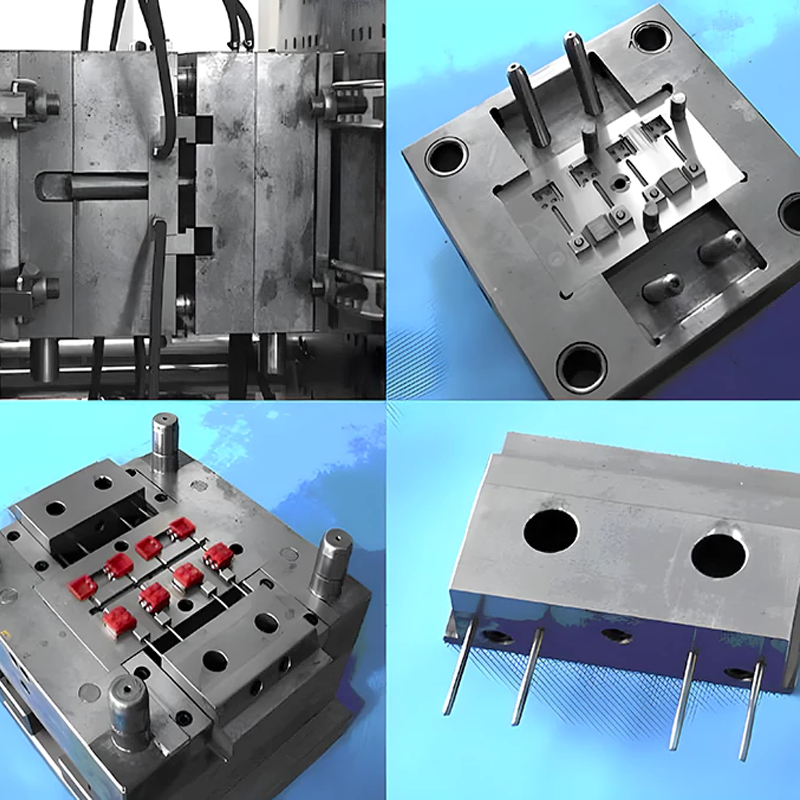
Injection Mold with Lateral Parting and Slider Mechanism
For molded parts that include undercuts or side holes—features that make part ejection difficult—a mold with lateral parting and a slider mechanism is essential. This mold design incorporates a side-mounted slider that moves laterally, creating undercuts during the molding process.
After the injection molding process, the core moves downward first. At this point, the oblique pin attached to the cavity plate forces the slider to shift outward. Simultaneously, the push rod mechanism activates, pushing the ejector plate to remove the molded part from the core. This mold is especially useful for complex parts that cannot be molded using standard two-plate designs due to their intricate geometry.
-
Injection Mold with Movable Molding Components
In some cases, plastic parts have specialized structures that necessitate the use of movable molding components. These components can include movable cores, cavities, inserts, threaded cores, or rings, which allow for greater flexibility in shaping the final product.
The key feature of this mold type is that the movable components shift along with the molded part during demolding. These components ensure that parts with complex geometries can be molded correctly and efficiently. For example, a threaded core may be used to create threaded plastic parts, while movable cavities can be employed to mold hollow structures or components with internal undercuts.
-
Automatic Thread Unloading Injection Mold
When dealing with plastic parts that have internal or external threads, traditional demolding methods may not be sufficient. To address this, an automatic thread unloading mold is often used. This mold incorporates a rotating threaded core or ring, which can be triggered to rotate during the mold opening process.
This rotation allows the threaded core or ring to release the molded part automatically, without the need for additional manual intervention. The use of a rotating mechanism or a dedicated drive system ensures that the part can be easily ejected without damaging the threads. Automatic thread unloading molds are particularly useful in applications where high volumes of threaded parts are required, such as in automotive and consumer electronics industries.
-
Hot Runner Injection Mold
The hot runner injection mold is a specialized mold that uses an advanced heating system to keep the plastic material in a molten state as it moves through the runners, sprues, and gates. Unlike traditional cold runner molds, hot runner systems eliminate the need for a runner system in the mold cavity, significantly reducing material waste and cycle times.
The primary advantage of a hot runner system is its ability to maintain the temperature of the material between the nozzle and the cavity, which helps to ensure consistent flow and reduced cycle times. Hot runner molds are ideal for high-precision applications where material conservation and consistent quality are crucial. These molds are commonly used in applications where the material needs to flow smoothly without solidifying prematurely, such as in thin-walled parts, automotive components, and medical devices.
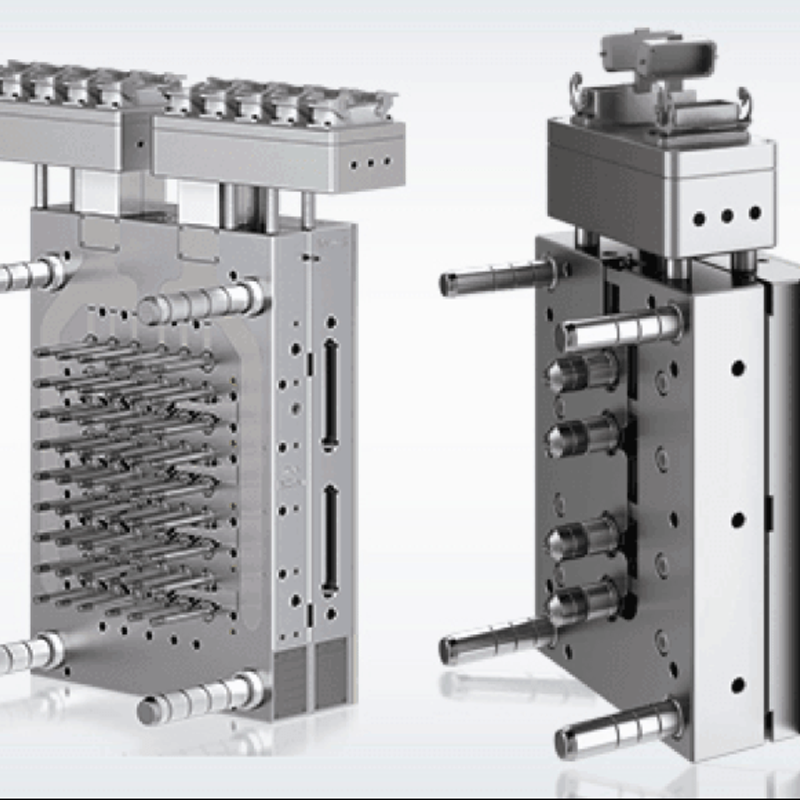
-
Right Angle Injection Mold
The right angle injection mold is used specifically in injection molding machines designed for angle injection molding. In this type of mold, the injection feed direction is perpendicular to the mold’s opening and closing direction, which differentiates it from other types of injection molds. The feed system is typically located along the sides of the core and cavity parts, with a constant cross-sectional area for the runner.
This type of mold is used for producing parts that require an injection flow path that avoids direct interference with the mold core. To prevent wear or deformation between the injection nozzle and the main runner inlet, a replaceable runner insert is often used. This mold type is especially beneficial when the injection machine’s nozzle cannot align directly with the cavity for a straight-in feed.
-
Injection Mold with Demolding Mechanism on the Mold Cavity Side
While many injection molds use a demolding device located on the mold core side, there are instances when it’s more practical to place the demolding mechanism on the mold cavity side. This is particularly the case for parts with complex geometries, which may not be easily ejected from the mold core side due to undercuts or intricate features.
In such cases, a demolding mechanism is installed on the cavity side, ensuring that the part can be ejected without interference. This configuration helps to overcome challenges related to part geometry and minimizes the risk of damaging delicate features during the ejection process.
Conclusion
The wide variety of injection molds available reflects the diverse range of parts and applications that injection molding can address. Each of the eight mold types outlined here offers unique advantages, allowing manufacturers to tailor the molding process to the specific needs of their product. Whether it’s a straightforward two-plate mold for mass production or a more complex hot runner system for precision applications, the right mold selection plays a critical role in optimizing efficiency, cost, and product quality.
As injection molding technology continues to evolve, we can expect these mold types to become even more advanced, incorporating innovative features to meet the growing demands of industries such as automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each mold type, manufacturers can make informed decisions, ensuring the highest levels of performance and product excellence.