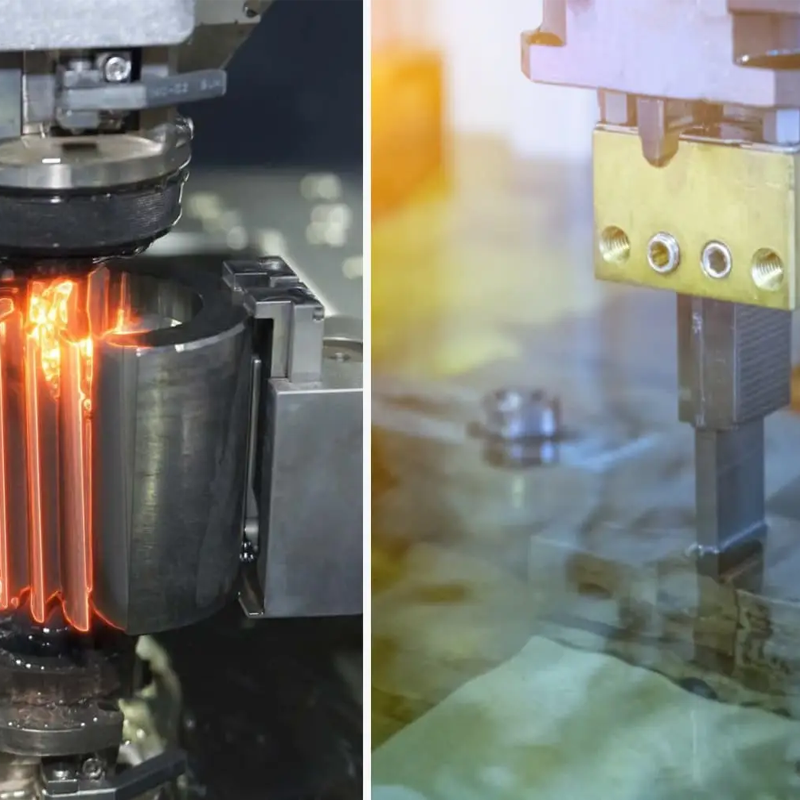
Hello, this is Sunny from Toolingsun. In today’s blog, we’re diving deep into the often-debated topic of Sinker EDM vs. Wire EDM machining. These two precision processes, while both under the umbrella of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), offer distinct advantages depending on the application. As manufacturers, understanding the differences between these methods is essential for optimizing your production process. At Toolingsun, we specialize in both Sinker EDM and Wire EDM services, providing tailored solutions for complex machining needs. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences, advantages, and applications of both techniques, helping you decide which is best suited for your next project.

What is Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)?
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), also known as spark erosion, is a non-conventional machining process that uses controlled electrical discharges (sparks) to remove material from conductive workpieces. Unlike traditional machining methods that require physical contact between the tool and the workpiece, EDM operates in a contactless environment. This makes it ideal for working with intricate designs and tough materials such as titanium, tungsten, and hardened steel.
During the EDM process, a high-frequency electrical current is passed between two electrodes: the tool (cutting electrode) and the workpiece (material being shaped). Both are submerged in a dielectric fluid—typically deionized water or hydrocarbon oil—to cool and insulate the process. The controlled sparks erode the material in a precise and highly controlled manner.
Key Steps of EDM:
- Precision Control: EDM machines adjust spark intensity and gap size to achieve highly detailed and accurate parts.
- Spark Generation: The voltage applied between the electrodes causes sparks to jump across the gap, eroding the workpiece material.
- Material Erosion: The sparks generate high temperatures that melt and vaporize small portions of the workpiece material.
- Debris Removal: The dielectric fluid flushes away the debris, ensuring continuous operation without obstruction.

Understanding Sinker EDM
Sinker EDM, also known as plunge or ram EDM, is a type of EDM that uses a custom-shaped electrode to create cavities or 3D shapes within a workpiece. It’s commonly used to manufacture intricate molds, dies, and other precision metal parts. Unlike other methods that involve linear cutting, Sinker EDM “plunges” the electrode into the material, layer by layer, until the desired cavity or shape is achieved.

How Sinker EDM Works:
A custom electrode, typically made of graphite, copper, or tungsten, is connected to a power supply and submerged in dielectric fluid along with the workpiece. A high-voltage pulse causes a spark to form between the electrode and the workpiece. This spark melts or vaporizes material, and the process is repeated until the desired cavity is formed.
The key benefits of Sinker EDM include the ability to create intricate geometries, blind holes, and cavities that other machining methods cannot achieve. It is widely used in the production of molds, dies, and aerospace components where high precision is critical.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sinker EDM
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Capable of creating complex shapes and blind cavities | Slower process compared to wire EDM |
| Effective for machining hard metals like steel, titanium, and alloys | Electrode wear over time |
| High precision with tolerances as tight as 0.0001 inches | Higher operational and setup costs |
| No physical contact between the tool and workpiece | Limited to electrically conductive materials |
Sinker EDM Applications
Sinker EDM is most effective in industries that require precision in creating complex cavities and molds. Some of its primary applications include:
| Industry | Specific Applications |
| Manufacturing | Injection molds, stamping dies, and rapid tooling |
| Automotive | Gears, internal engine cavities |
| Medical | Implants, orthopedic devices |
| Aerospace | Turbine components, aircraft frames |
| Research | Prototypes, R&D projects |
Exploring Wire EDM
Wire EDM, also known as wire-cut EDM, is a similar non-contact process that uses a thin wire (usually brass or copper) to erode the workpiece along a predetermined path. The wire moves continuously in both the X and Y axes to cut the material, following a precisely programmed contour.

How Wire EDM Works:
The wire is continuously fed from a spool and passes through the workpiece with electric sparks created between the wire and the material. The process uses deionized water to cool the cutting area and wash away debris. Because the wire is extremely thin (sometimes as thin as 20 microns), Wire EDM is ideal for cutting delicate shapes with micron-level precision.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wire EDM
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| High precision and fine finishes | Higher setup cost |
| No mechanical stress on the workpiece | Only works with conductive materials |
| Ideal for delicate and fragile materials | Formation of oxide layers on some materials |
| Faster than Sinker EDM for certain applications | May be slower for thicker materials |
Wire EDM Applications
Wire EDM is perfect for industries that require extremely precise cuts and profiles, particularly when working with hard materials. Common applications include:
| Industry | Specific Applications |
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, lightweight intricate parts |
| Medical | Microchips, sensors, and connectors |
| Automotive | Engine cylinders, complex structural components |
| Manufacturing | Precision dies and molds |
Key Differences Between Sinker EDM and Wire EDM
After examining the processes, let’s compare the two methods in terms of their machining process, capabilities, and suitability for different applications.
| Factor | Sinker EDM | Wire EDM |
| Machining Process | Custom-shaped electrode “sinks” into the material to create 3D shapes. | Thin wire cuts along a 2D path, suitable for precise profiles. |
| Geometry | Ideal for complex 3D geometries and deep cavities. | Best for 2D profiles and fine details. |
| Tooling | Custom CNC-made electrode, typically graphite or copper. | Continuous feed of thin wire, usually brass or copper. |
| Surface Finish | Rougher surface finish; may require post-processing. | Finer, smoother finish with less post-processing. |
| Material Thickness | Suitable for thicker materials and blind cavities. | Ideal for thinner materials, can cut up to several inches. |
| Precision | High precision with tolerances up to 0.0001 inches. | High precision, often exceeding 0.00005 inches. |
| Applications | Ideal for molds, dies, and 3D cavities. | Best for intricate 2D profiles and fine tolerances. |
Choosing the Right EDM Process
The choice between Sinker EDM and Wire EDM depends on several factors, including material type, part geometry, surface finish requirements, and production volume. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide which process is best suited for your needs:
| Factor | Sinker EDM | Wire EDM |
| Material Type and Thickness | Best for thicker, tougher materials like steel and titanium. | Best for thin materials requiring fine detail. |
| Part Geometry | Suitable for creating deep, complex shapes, molds, and dies. | Best for precise 2D profiles and small, detailed features. |
| Surface Finish | May require additional finishing steps. | Typically provides a smoother finish. |
| Tolerance | Extremely tight tolerances, ideal for precision parts. | Best for parts with high precision and fine features. |
| Production Volume | Ideal for larger runs with less complexity. | Suitable for low-volume, high-precision projects. |
| Cost Considerations | More economical for large-scale production. | Typically more expensive due to longer processing times. |
Conclusion
Both Sinker EDM and Wire EDM offer exceptional precision and unique capabilities for different machining applications. If you need to create deep, intricate shapes in hard or thick materials, Sinker EDM is your best option. On the other hand, if your project demands fine detail and micron-level precision, especially in thinner materials, Wire EDM is the way to go.
At Toolingsun, we provide advanced EDM services tailored to your specific manufacturing needs. Whether you’re creating complex molds, intricate parts, or precise tooling, our team has the expertise to deliver top-notch results with both Sinker EDM and Wire EDM technologies. Contact us today to discuss how we can help streamline your next project with our state-of-the-art EDM machining solutions.