When investing in a plastic injection mold—whether for a new product line or to improve an existing one—it involves a substantial financial outlay. The design and manufacturing process requires meticulous attention to ensure high quality, operational efficiency, and long-term durability. As an expert mold manufacturer, we recognize the intricacies of this process and understand the key factors that buyers must consider to maximize their return on investment.
In this blog, we will delve into the essential components of plastic injection mold design, focusing on how to select the ideal mold for your specific project. Whether you are a first-time buyer or a seasoned professional, these insights will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions and achieve your production objectives.

-
Defining Your Product Requirements
Before initiating the mold design process, it’s crucial to have a detailed understanding of your product’s specifications. The intended use of the part heavily influences various aspects of mold design, including material selection, mold complexity, and the structure of the cavities.
Material Selection
The choice of plastic material has a significant impact on the mold design. Different materials come with unique properties like melting temperature, shrinkage rates, and cooling times. For example:
– ABS is known for its strength and durability but has a high shrinkage rate.
– Polypropylene (PP) is lightweight and flexible but may require special mold considerations for thin-walled components.
– Polycarbonate (PC) offers exceptional impact resistance but requires molds that can withstand high temperatures.
Collaborating closely with your mold manufacturer during the material selection process ensures the mold design will accommodate the material’s characteristics, helping to mitigate issues like warping or sink marks.
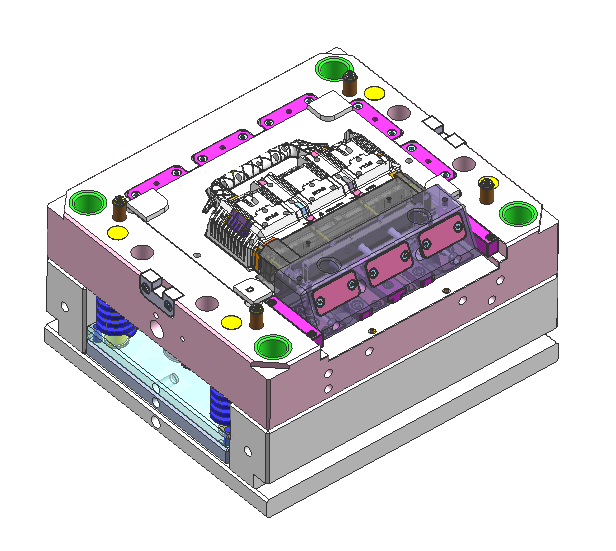
Part Complexity
The complexity of your part—including intricate features, undercuts, or tight tolerances—dictates the type of mold you’ll need. More complex parts may require multi-cavity molds or special features such as lifters or side-actions to ensure proper ejection and fill. The higher the part complexity, the more advanced the mold design, which can influence both cost and lead time.
-
Choosing the Right Mold Type and Configuration
There are different types of plastic injection molds, each suited for specific production requirements. Selecting the right mold is key to optimizing cost, efficiency, and production capacity.
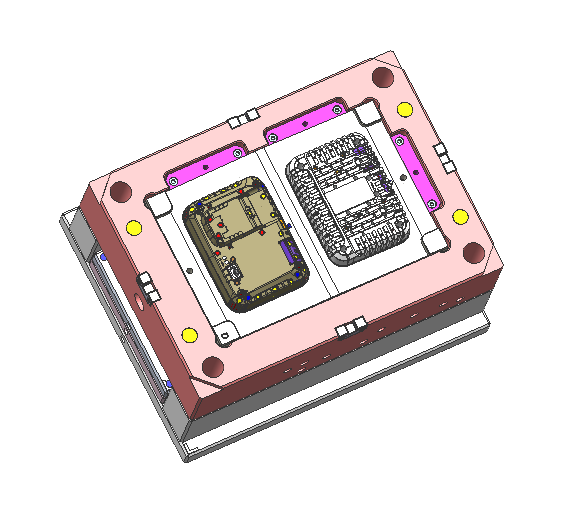
Single-Cavity vs. Multi-Cavity Molds
– Single-cavity molds are suited for low-volume production runs, prototypes, or testing new designs. They are simpler and less expensive but may limit output due to slower cycle times.
– Multi-cavity molds produce multiple parts per cycle, improving production efficiency. However, they are more complex and costly to manufacture, requiring precise balancing of cavity pressures to ensure consistent part quality.
Hot Runner vs. Cold Runner Systems
– Cold runner molds are more cost-effective but generate more material waste, as the leftover material in the runner needs to be either discarded or recycled.
– Hot runner molds maintain the plastic in molten form within the runner, reducing waste and shortening cycle times. Although they have a higher initial cost, they offer substantial savings for high-volume production runs.
Consulting an experienced mold designer can help determine the most suitable mold configuration based on your production targets and material needs.
-
Prioritizing Mold Quality and Durability
Ensuring your mold is built to last is essential for minimizing downtime and maintaining consistent production. The quality of a mold depends on the materials used, precision manufacturing, and stringent quality control measures.
Mold Base and Core Materials
High-performance molds are typically constructed from durable metals like hardened steel (e.g., H13, S136) or pre-hardened steel (e.g., P20). The choice depends on production volume:
– Hardened steel molds offer excellent wear resistance and are ideal for long production runs, but they come with higher upfront costs.
– Pre-hardened steel molds are cost-effective for short to medium runs but may degrade faster in high-volume applications.
For low-volume or prototype molds, aluminum can be an option due to its lower cost and ease of machining, though it lacks the durability of steel.
Cooling Systems
An efficient cooling system is vital to reducing cycle time and maintaining part quality. Poor cooling can lead to warping or shrinkage. Well-designed molds integrate cooling channels that ensure uniform temperature distribution, improving cycle time and product consistency.

-
Achieving Precision and Tight Tolerances
Plastic injection molding requires a high level of precision, particularly for parts with tight tolerances. The accuracy of the mold directly impacts the dimensional consistency and quality of the final product.
Tolerance Considerations
Mold designs must accommodate factors such as plastic shrinkage and thermal expansion to consistently achieve precise dimensions. Close collaboration with your mold manufacturer ensures that the desired tolerances are met, particularly for high-specification components.
Surface Finish
Surface finish requirements also play a critical role in mold design. If your product requires a high-gloss finish, mold cavities will need to be polished to a mirror-like surface. Textured finishes require specific mold treatments. The finish not only affects aesthetics but also functionality and ease of ejection.
-
Maintenance and Longevity
Investing in a high-quality mold is only the first step. Regular maintenance is crucial to extending the mold’s lifespan and ensuring consistent part production.
Maintenance Planning
Establishing a preventive maintenance plan with your mold manufacturer can reduce wear, prevent breakdowns, and minimize unexpected downtime. Routine activities such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection of critical components—like ejector pins and cooling lines—are vital for maintaining optimal mold performance.
-
Cost vs. Value
The cost of a plastic injection mold depends on several factors, including material selection, mold complexity, cavity count, and runner type. It’s important to balance upfront investment with long-term value.
Balancing Initial Cost with Longevity
While high-quality molds may come with a higher price tag, they often result in lower long-term costs through reduced maintenance, improved durability, and better part quality. Conversely, opting for a cheaper mold may lead to higher long-term costs due to frequent repairs or early replacement.

-
Custom Mold Solutions
One of the major advantages of working with a professional mold manufacturer is the ability to develop fully customized molds tailored to your exact specifications. Custom solutions provide the flexibility to meet both functional and aesthetic requirements, ensuring optimal performance for your application.
Conclusion
Purchasing a plastic injection mold is a significant investment that requires thoughtful consideration of your production requirements, part specifications, and budget. By carefully evaluating factors such as material selection, mold type, quality, precision, and costs, you can make informed decisions that lead to success in your injection molding projects. Working with an experienced mold manufacturer will help you design the ideal mold and streamline your production process.
Taking the time to focus on mold design upfront will lead to higher-quality products, greater production efficiency, and long-term savings. Whether producing simple parts or complex components, a well-crafted mold is the foundation of success in plastic injection molding.

